Every researcher knows the frustration: you design a survey, deploy it to hundreds of respondents, and realize too late that your questions didn't probe deeply enough on the insights that matter most.
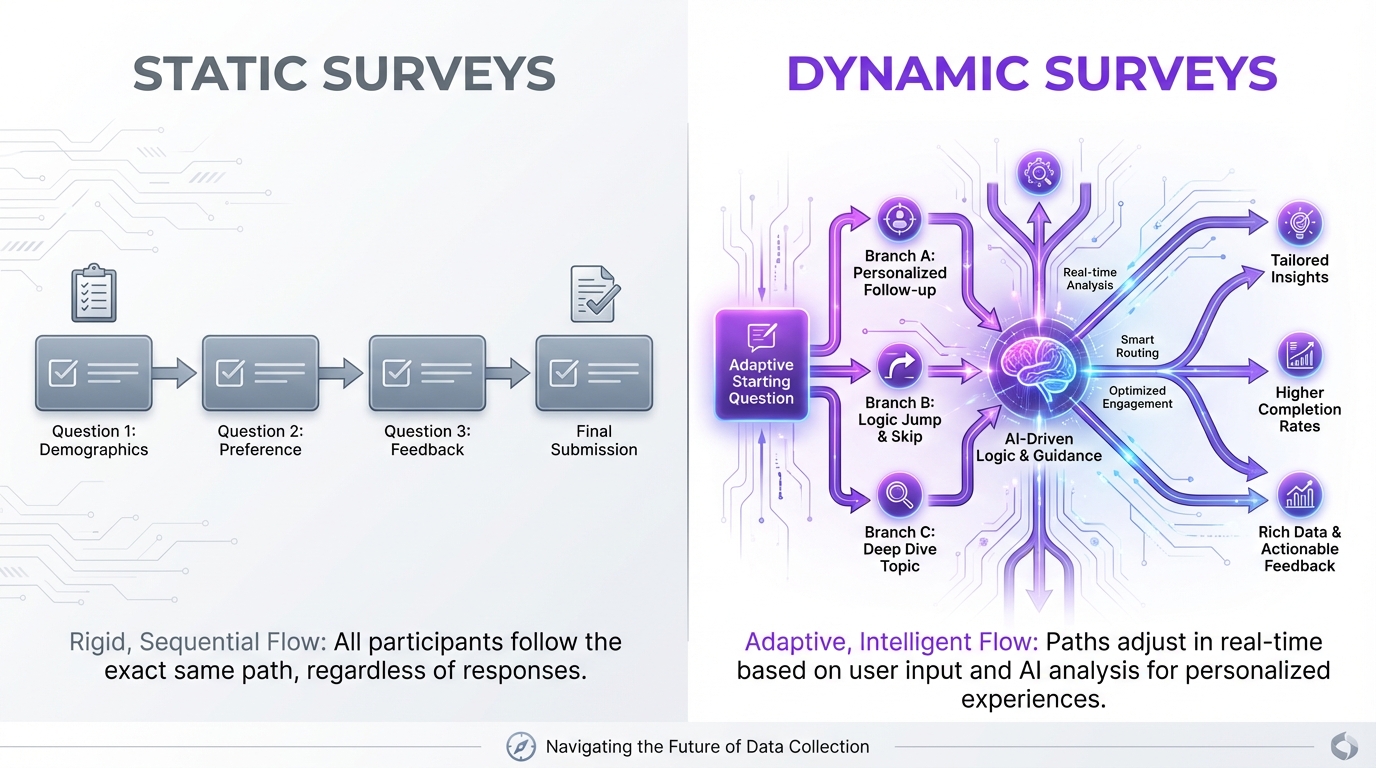
Traditional surveys are static. Everyone sees the same questions in the same order. The structure is fixed before the first response.
Dynamic surveys change that. They adapt based on responses, probing deeper where interesting answers emerge and skipping irrelevant questions entirely.
But which approach is right for your research? Let's break it down.
How Static Surveys Work
Static surveys follow a predetermined path:
- Researcher designs questions
- Establishes question order
- Builds skip logic for basic branching
- Deploys identical survey to all respondents
- Analyzes responses after collection completes
Strengths:
- Standardized data collection
- Easy quantitative analysis
- Predictable completion time
- Simple to validate and reproduce
Weaknesses:
- Can't probe interesting responses deeper
- Includes irrelevant questions for some respondents
- Misses emergent themes
- Limited qualitative depth
How Dynamic Surveys Work
Dynamic surveys use AI to adapt in real-time:
- Researcher establishes research objectives and seed questions
- AI generates initial questions aligned with objectives
- Based on each response, AI determines optimal follow-up
- Survey branches intelligently toward insights
- Analysis happens continuously, informing subsequent questions
Strengths:
- Probes interesting responses automatically
- Skips irrelevant sections intelligently
- Surfaces emergent themes
- Combines quantitative and qualitative depth
Weaknesses:
- Less standardized across respondents
- More complex analysis requirements
- Requires AI capabilities
- Variable completion time
The Case for Static Surveys
Static surveys remain the right choice in several scenarios:
Benchmarking and Tracking
When you need to compare results over time or across groups, standardization matters. Static surveys ensure everyone answers identical questions, making longitudinal and cross-sectional comparisons valid.
Example: Annual employee engagement surveys that track changes year-over-year.
Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Some research contexts require demonstrable standardization. FDA clinical trials, academic replication studies, and certain compliance surveys need documented consistency.
Example: Patient-reported outcome measures in clinical research.
Simple, Focused Inquiries
For straightforward questions with limited branching needs, static surveys are simpler and sufficient.
Example: Event feedback with basic satisfaction questions.
Statistical Analysis Plans
When your analysis plan requires specific sample sizes for specific questions, static surveys ensure you collect what you need.
Example: Conjoint analysis requiring every respondent to evaluate specific trade-offs.
The Case for Dynamic Surveys
Dynamic surveys excel when insight depth matters more than standardization:
Exploratory Research
When you don't know exactly what you're looking for, dynamic surveys can discover themes you wouldn't have thought to ask about.
Example: Understanding why customers churned when exit interviews reveal unexpected patterns.
Complex, Variable Topics
When respondents have vastly different experiences, forcing everyone through identical questions wastes their time and your opportunity.
Example: Product feedback where some users use features others have never discovered.
Qualitative Depth at Quantitative Scale
When you want to understand "why" from many respondents, not just "what" percentage selected option B.
Example: Understanding customer jobs-to-be-done across segments.
Limited Respondent Attention
When you have limited time with respondents, spending that time on relevant questions maximizes insight.
Example: Busy executives who will give you 5 minutes, not 15.
Practical Comparison
| Factor | Static Survey | Dynamic Survey |
|---|---|---|
| Standardization | High | Moderate |
| Qualitative depth | Limited | High |
| Completion time | Predictable | Variable |
| Respondent experience | Can feel irrelevant | Feels personalized |
| Analysis complexity | Straightforward | Requires synthesis |
| Emergent insights | Rare | Common |
| Best sample size | Any | 50+ for pattern detection |
How Dynamic Surveys Actually Work
Let's trace an example:
Research objective: Understand why customers don't complete purchases.
Seed question: "You added items to your cart but didn't complete the purchase. What happened?"
Response: "The shipping cost was too high."
AI-generated follow-up: "What shipping cost would have been acceptable for this order?"
Response: "Under $10."
AI-generated follow-up: "If we offered free shipping on orders over $75, would that have changed your decision?"
Response: "Yes, definitely. I would have added more items."
AI-generated follow-up: "What additional items would you have considered adding?"
This conversation continues until the AI has thoroughly explored the respondent's experience. Meanwhile, another respondent who said "I found a better price elsewhere" gets a completely different follow-up path.
Analyzing Dynamic Survey Data
Because dynamic surveys generate different data for different respondents, analysis requires different approaches:
Thematic Analysis
AI-assisted analysis identifies themes across varied responses, grouping similar insights regardless of which specific questions generated them.
Quote Extraction
Direct quotes organized by theme provide compelling qualitative evidence.
Quantitative Overlay
Even with varied paths, you can quantify: "47% of respondents mentioned price sensitivity, regardless of which questions surfaced this theme."
Segment Comparison
Compare themes across respondent segments to identify where experiences diverge.
The Hybrid Approach
Many researchers find value in combining approaches:
Fixed opening questions: Establish baseline demographics and key quantitative measures.
Dynamic middle section: Explore experiences with adaptive follow-ups.
Fixed closing questions: Standardized summary measures for comparison.
This structure gives you standardized data where you need it and qualitative depth where it matters most.
Implementation Considerations
Survey Length
Dynamic surveys typically take longer per respondent (more probing means more questions), but respondents often report higher engagement because questions feel relevant.
Set expectations appropriately and consider incentives for the additional time investment.
Interviewer Effect
Because AI determines follow-up questions, you introduce the AI's "judgment" into data collection. This is similar to human interviewer effects in qualitative research—something to acknowledge and document.
Reproducibility
Dynamic surveys are harder to reproduce exactly because the conversation depends on responses. For academic research, document the AI's decision-making parameters and seed questions clearly.
Analysis Capacity
Ensure you have capacity to analyze qualitative data at scale. AI-assisted analysis tools are essential for processing hundreds of unique conversations.
Choosing Your Approach
Choose static surveys when:
- Standardization is legally or methodologically required
- You're doing longitudinal tracking
- Your questions are simple and universal
- Statistical analysis plans require specific data structures
Choose dynamic surveys when:
- You're exploring to discover insights
- Respondent experiences vary significantly
- Qualitative depth matters more than standardization
- You want to maximize limited respondent attention
Choose hybrid when:
- You need both standardized metrics and qualitative depth
- Different sections of your research have different needs
- You're transitioning from static surveys and want to compare approaches
Getting Started with Dynamic Surveys
If you're new to dynamic surveys:
- Start with a clear research objective (not just questions)
- Develop seed questions that open conversations
- Pilot with 10-15 respondents to see how AI probing works
- Review conversations to ensure AI follow-ups align with research goals
- Iterate on seed questions and objectives based on pilot findings
- Scale once you're confident in the approach
Ready to see dynamic surveys in action? Explore Qualz.ai's dynamic survey capabilities or try a live demo to experience adaptive questioning yourself.